Oncology

What Is Cancer?
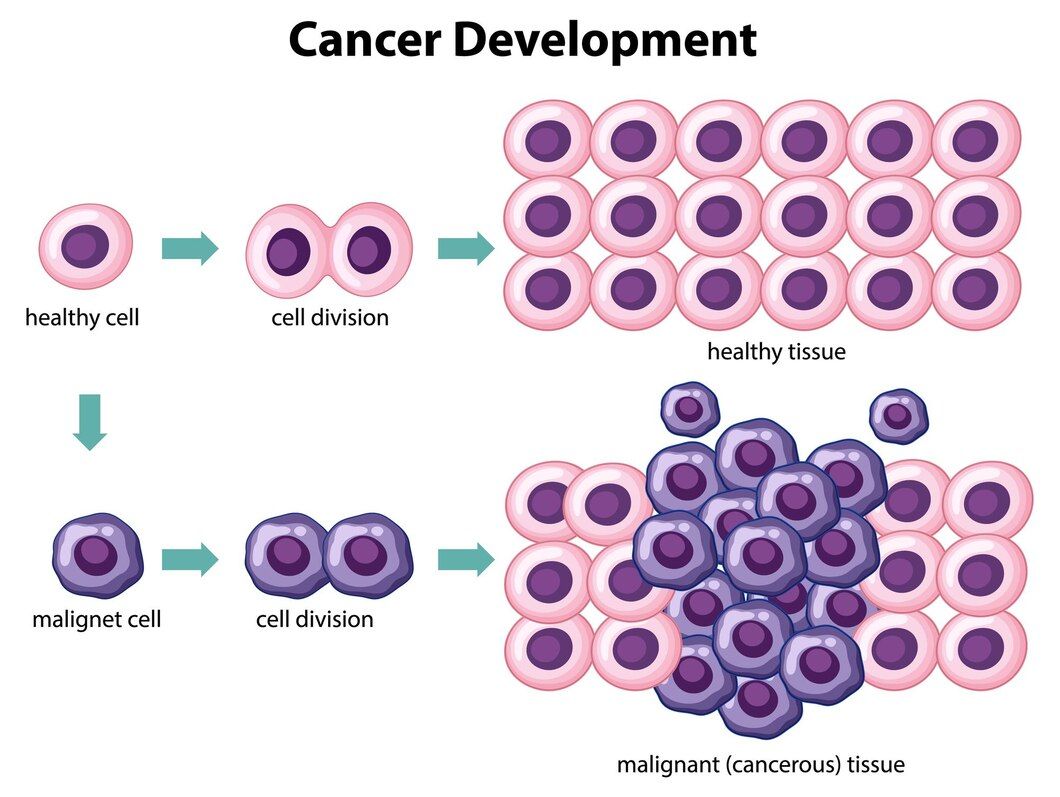
When cells of body tissues undergo a change beyond their routine characteristics and proliferate uncontrollably, it can be defined as cancer. Cancer, considered one of the most serious diseases of the era, ranks second among the causes of death in Turkey. The rate at which cancer spreads to neighbouring tissues is quite high.
In the treatment processes within the scope of medical oncology, drug applications given intravenously or orally stand out. However, these applications naturally vary depending on the type of cancer. Similarly, the treatment plan to be carried out by the specialist physician also varies according to the type of cancer cell, the organ it has originated from, and the region it has spread to. Here, the important thing is to minimize the risks of the disease recurring. For this purpose, practices such as adjuvant, neoadjuvant, and palliative care are utilized.
Medical Oncology
Cancer is a global health problem that is widely prevalent worldwide and poses a threat to public health. Oncology is the medical unit concerned with the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of cancer. The field of oncology is divided into different sub-disciplines such as surgical oncology, radiation oncology, and medical oncology. Significant advancements are being made every day in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Medical oncology, in its most general sense, is a department where cancer is treated with medication. Chemotherapy encompasses treatment methods using drugs to destroy cancer cells. Various methods such as chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy are used in the medical oncology department for cancer treatment purposes.


What is Medical Oncology?
Cancer is defined as the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells due to damage to DNA in the cell. Cancer has become a very serious public health problem that is increasing worldwide. The field of oncology is divided into different branches and deals with the treatment of cancer. Medical oncology, also known as medical oncology, is an important medical unit that deals with the treatment of cancer with drugs.
Medical oncology encompasses not only the treatment of cancer patients but also cancer prevention, screening, and early diagnosis practices. This means that every stage of cancer concerns the medical oncology department. Additionally, in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, collaboration is made with various fields such as surgery or radiology, and a multidisciplinary approach is applied on a personalized basis.
The treatment method in the medical oncology department is carried out with drug applications administered intravenously or orally. However, these applications may vary depending on the course of the disease and the type of cancer. Treatment planning varies according to the cell type of cancer, the organ where it originated, and the region it has spread to. Treatment can be applied alone with drug therapy or in combination with other treatment methods.
The medical oncology department generally works in collaboration with radiology, pathology, radiation oncology, nuclear medicine, and other internal medicine units. In addition to treatment-oriented studies, necessary tests and examinations can be performed for individuals suspected of cancer. Early diagnosis of cancer is also important for treatment. In the medical oncology department, antibody therapies, chemotherapy, hormone therapies, and personalized treatment methods are applied.
Which Diseases Does Medical Oncology Deal With?
Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth or proliferation of cells in any part of the body. Symptoms and treatment of cancer vary depending on the type of cancer. Expert physicians in the field of medical oncology prepare a treatment plan according to the types of cancer and the individual’s needs.
We can touch upon the main types of diseases falling under medical oncology as follows:
- Lymphoma, leukaemia: Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. Leukaemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, causing an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
- Breast cancer: Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the cells of the breast. It can occur in both men and women but is more common in women.
- Brain cancer: Brain cancer refers to abnormal growths of cells in the brain. There are various types of brain tumours, some of which are cancerous (malignant) and others are non-cancerous (benign).
- Various types of cancer such as lung, stomach, and colon cancer: These cancers originate in different parts of the body. Lung cancer affects the lungs, stomach cancer occurs in the stomach lining, and colon cancer develops in the colon or rectum.
- Melanoma, sarcomas: Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the cells responsible for producing pigment in the skin. Sarcomas are cancers that develop in the connective tissues, such as bones, muscles, cartilage, or blood vessels.
- Head and neck cancers: These cancers can occur in various parts of the head and neck, including the throat, mouth, nose, sinuses, and salivary glands. They often affect the mucosal surfaces lining these areas.
- Prostate cancer: Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, which is a part of the male reproductive system. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men.
Each of these illnesses presents unique challenges and treatment approaches, and early detection and appropriate medical care are essential for better outcomes.
Many types of cancer fall under the purview of medical oncology, such as those mentioned above. Medical oncologists are often the specialists that individuals with suspected cancer turn to initially. Medical oncology specialists closely follow up not only the cancer treatment but also the post-treatment processes.
Just like worldwide, cancer is one of the most threatening diseases to human life in Turkey. The incidence rates of cancer reflect the seriousness of the situation.
New treatment methods are being developed against cancer disorders, which are gaining increasing importance universally every year.
In Turkey, the most common types of cancer include prostate, breast, lung, rectum, and stomach/pancreas cancers. Medical Oncology units play a significant role in the coordination process of individuals diagnosed with cancer.
At our partner hospitals “Medical Oncology” unit handles the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up processes of cancer patients. When necessary, collaborative actions are taken with all units, and joint decisions regarding the patient’s treatment schedule are made. The medical oncology unit is sometimes referred to as “medical oncology.”
Radiation Oncology
Cancer is known as the second leading cause of death worldwide. Nowadays, the frequency of cancer cases is increasing day by day. The medical unit dealing with cancer is oncology. Radiation oncology is an important medical specialty that investigates the effects of ionizing radiation on cancer cells and tumours and uses ionizing radiation for treatment purposes.
Treatment with radiotherapy is applied in the radiation oncology department. Radiation oncology uses two main treatment methods known as radiotherapy and radiation surgery in cancer treatment. In addition, in the radiation oncology department, the effect of ionizing radiation on cancer and the behaviour patterns of tumours are investigated.
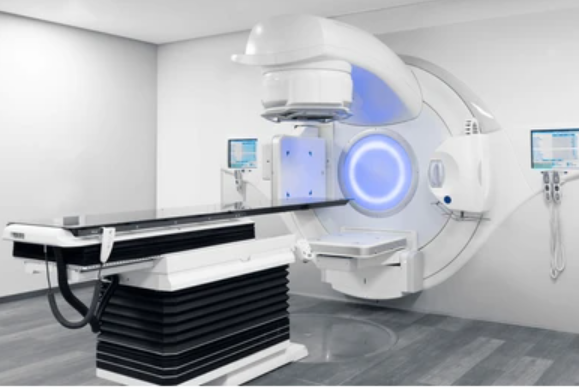
What is Radiation Oncology?
The beam therapy (radiotherapy) applied in the radiation oncology department is seen as an important treatment method for cancer. Radiotherapy, which can be used alone in cancer treatment, can also be applied in conjunction with other treatment methods. Known as beam therapy, radiotherapy is recognized as an innovative and modern treatment method effective in cancer treatment.
With radiotherapy, cancer cells are targeted to be damaged by radiation beams, aiming to treat cancer in this way. Such radiotherapy applications fall within the scope of the expertise of the radiation oncology department, and the treatment practices conducted with this method are carried out by radiation oncology clinics and specialists.
Radiation oncology is an important medical unit that investigates the effects of all kinds of radiation therapy that can be performed using ionizing radiation on cancer cells and tumours and conducts research in this field. In this way, the use of high doses of radiation energy for treatment purposes is called ‘beam therapy’ or ‘radiotherapy’. Especially, high-dose radiation therapy with radiotherapy has the function of destroying or inhibiting the proliferation of cancer cells.
The management of the radiotherapy process is carried out by specialist physicians in radiation therapy. The radiation oncology specialist determines the type of treatment needed by the patient and plans the treatment process. The radiation oncology specialist conducts the treatment process in collaboration with the necessary specialists. Approximately 70% of all cancer patients may require radiation oncology treatment methods at any stage of treatment.
Radiation therapy is also known as ‘beam therapy’ in public. In the radiation oncology department, specialists from various medical units such as radiation oncologists, radiation therapy technicians, nurses, medical physicists, dietitians, and psychologists can provide services. Moreover, important issues such as investigating and staging how much the tumour has spread are evaluated with a multidisciplinary approach for treatment processes.
The duration of radiation therapy sessions can vary from a few minutes to several hours. The area of the skin exposed to radiation therapy can become sensitive and easily irritated, especially. Generally considered a painless procedure, radiation therapy usually has temporary side effects. However, these side effects may vary depending on the region of the body undergoing treatment. The primary goal of radiation therapy is to destroy cancer cells while causing as little harm as possible to healthy cells.
Which Diseases Does Radiation Oncology Deal With?
Treatment can be applied to all types of cancer in the radiation oncology medical unit. Approximately 50-70% of all cancer patients can benefit from radiation oncology treatment methods at any stage of the diseases.
Some important diseases that the radiation oncology department deals with can be listed as follows:
-
- Brain tumours
- Breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Skin cancer
- Larynx cancer
- Gynecological cancers
- Bladder cancer
- Lung cancer
- Childhood tumours
- Lymphomas
- Digestive system cancers
- Soft tissue tumours
- Head and neck cancers
- Rectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
Additionally, the possible side effects of radiotherapy applied within the scope of the radiation oncology department may vary depending on factors such as the region where the treatment is applied, the dose of radiation, the overall health status of the individual, and the duration of treatment.
While the duration of radiotherapy may not be the same for every patient, there are many factors that determine the duration of treatment for the patient.
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in cancer.
If you have any questions or if you want a consultation feel free to contact us.
*Pharmalps is not a clinic*
**Pharmalps offers consultancy services for health tourism**

